Modernizing legacy Java applications is no longer just a technical upgrade; it’s a strategic business priority. Companies that continue to rely on outdated Java systems face serious challenges, including limited scalability, recurring security risks, rising maintenance costs, and reduced agility. These issues don’t just slow down operations; they hold back innovation and competitiveness.
In the past, modernization was a slow, manual process involving lengthy code reviews, dependency updates, and architectural redesigns. But things have changed. AI-powered development tools are revolutionizing how modernization occurs. They automate code analysis, recommend smart refactoring strategies, and speed up upgrades, helping businesses transform legacy systems into secure, high-performing applications faster and with greater precision than ever before.
This blog discusses the need for modernizing legacy Java applications and explores how AI can accelerate this process.
Key Challenges in Legacy Java Systems
Legacy Java systems often face significant challenges, such as
- Outdated versions (Java 6/7/8) with deprecated APIs and Outdated frameworks (e.g., Struts 1, EJB 2.0).
- Monolithic architectures that hinder scalability, tight coupling, and poor modularity.
- Security gaps due to old libraries.
- High technical debt and poor documentation.
- Security vulnerabilities
- Lack of maintainability and developer onboarding issues
Why Modernizing Legacy Java Applications Matters
Modernization objectives typically include:
- Upgrading to Java 17 or higher.
- Migrating from monoliths to microservices.
- Adopting frameworks like Spring Boot and Jakarta EE.
- Improving code quality, maintainability, and performance.
How AI Transforms Java Modernization
AI assistants leverage machine learning models trained on millions of code examples to analyze legacy code for anti-patterns and deprecated APIs, suggest refactoring strategies aligned with best practices, automate repetitive tasks such as syntax updates and dependency migrations, generate unit tests for improved coverage, and provide real-time recommendations during development. This means developers can focus on architecture and business logic, while AI handles the heavy lifting.
Step-by-Step Modernization Approach with AI
- Assess Your Legacy Codebase using AI-powered static analysis tools to detect deprecated APIs, security vulnerabilities, and performance bottlenecks.
- Upgrade Java Version with AI assistants that suggest replacements for deprecated methods and update syntax for newer Java features.
- Refactor Monolithic Architecture by leveraging AI to recommend modularization strategies and generate boilerplate code for microservices.
- Migrate Frameworks using AI tools to automate large-scale transformations, such as moving from Struts or JSF to Spring Boot.
- Enhance Testing with AI-generated unit and integration tests and predictive edge case analysis.
- Continuous Validation by integrating AI into CI/CD pipelines for automated code reviews, regression detection, and performance optimization.
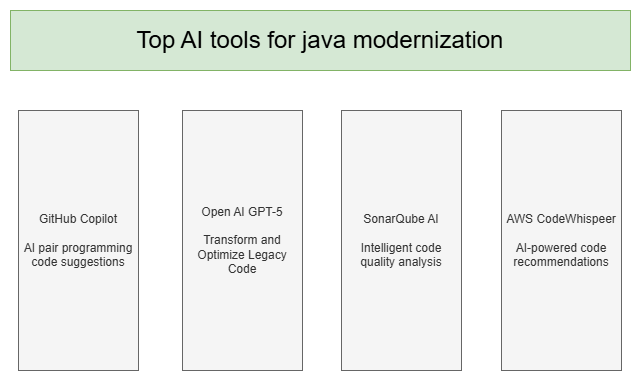
Top AI Tools for Faster Java Application Refactoring
AI-powered tools are revolutionizing Java modernization by automating code analysis, refactoring, and enhancing quality. These solutions help accelerate migration from legacy systems to modern architectures with minimal manual effort.
The following are the top AI tools driving Java modernization:
Best Practices for Safe and Scalable Modernization
While AI tools accelerate modernization, adhering to best practices ensures consistency, efficiency, quality, and minimizes risks in achieving desired outcomes-
- Human-in-the-Loop: Always review and test AI-generated code before deployment.
- Security: Ensure AI tools comply with enterprise security policies. Run AI tools in secure environments and scan outputs for vulnerabilities.
- Incremental Approach: Modernize in phases to reduce risk. Start with low-risk modules and use gradual rollout strategies.
- Context Understanding: AI may lack full knowledge of legacy architecture and business logic.
- Performance Optimization: AI suggestions might not be tuned for existing infrastructure.
- Performance Optimization: AI suggestions might not be tuned for existing infrastructure
- Establish Guardrails: Enforce coding standards and restrict AI access to sensitive code.
- Continuous Monitoring: Track performance and maintain audit logs of AI-driven changes.
Coforge’s XJava Accelerator: Modernizing Java at Scale
Accelerate your Java upgrade and modernization journey with Coforge’s proprietary XJava Accelerator - developed by our Product Engineering team within the Engineering Group. XJava is designed to enable seamless migration from older Java versions, such as 6 or 7, to modern versions, such as Java 17 or 21. Here is the screenshot representing the key capabilities of the XJava Accelerator.
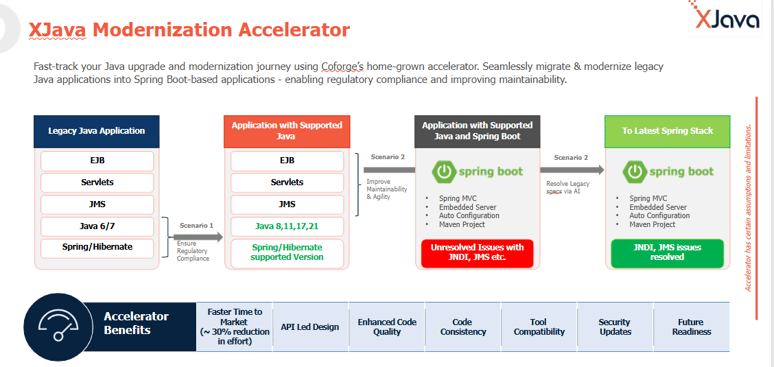
Effortlessly transform legacy EJB and servlet-based applications into scalable, cloud-ready Spring Boot architectures. By leveraging automation, proven frameworks, and industry best practices, we ensure a smooth, risk-free migration that maximizes speed and efficiency. Our approach not only modernizes your technology stack but also enhances performance, maintainability, and scalability.
With built-in compliance capabilities, you stay ahead of regulatory standards while reducing technical debt and improving agility. Modernizing with Coforge means faster time-to-market, future-ready systems, and a technology landscape built on innovation and reliability. Here is the screenshot of the key utility of the XJava Accelerator.
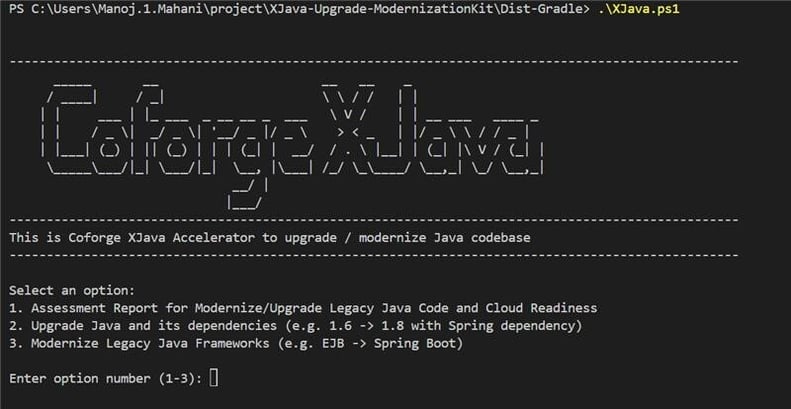
How Coforge Helps Enterprises Modernize with AI
Coforge accelerates enterprise legacy system modernization by combining AI-powered tools with proprietary accelerators. We leverage GitHub Copilot for AI-assisted coding, OpenAI GPT-5 to simplify and modernize complex logic, SonarQube AI for intelligent code quality checks, and AWS CodeWhisperer for secure, context-aware recommendations - delivering faster modernization with reduced risk and technical debt.
Our innovation, the XJava Accelerator, is purpose-built for Java application transformation, automating code restructuring, enhancing performance, and ensuring scalability for future-ready architectures.
By integrating AI-driven capabilities like automated refactoring, vulnerability detection, and predictive insights, we streamline workflows and minimize downtime. This holistic approach empowers organizations to achieve agility, resilience, and continuous innovation while evolving legacy systems into modern digital ecosystems.
FAQs:
AI can automate 40–70% of modernization tasks, but architecture decisions and business logic validation still require human expertise.
It detects deprecated APIs, suggests modern alternatives, updates syntax, and automatically fixes compatibility issues. .
AI can identify modularization opportunities, but final domain boundaries require human-driven domain analysis.
Yes - if combined with human review, automated tests, security scanning, and CI/CD validation.
It automates Java upgrades, EJB/servlet migration, Spring Boot transformation, and cloud-ready refactoring using proven modernization patterns.
What Goes Wrong:
- AI misinterprets complex business logic and produces syntactically correct but functionally incorrect code.
- Auto-generated microservices boundaries may not reflect real-world domain models.
- Deprecated API replacements may miss edge cases, causing runtime instability.
- Automated test generation may create shallow tests that fail to cover high‑risk logic.
- Framework migration tools can overgeneralize patterns, leading to broken integrations.
- Over‑dependence on AI can lead to technical debt if not reviewed and governed carefully.
Key Takeaways:
- AI drastically reduces effort in Java version upgrades, framework migration, and code cleanup.
- Automated refactoring works best when paired with clear architectural direction and human validation.
- Legacy monolith decomposition improves scalability but requires more than automated pattern recognition.
- AI-generated testing enhances stability and cuts regression cycles during modernization.
- Coforge’s XJava Accelerator strengthens modernization through automation, compliance, and cloud‑ready design.
- Combining commercial AI tools with proprietary accelerators delivers measurable speed and quality improvements.
Glossary:
- Static Code Analysis - Automated review of code to find vulnerabilities, anti‑patterns, and quality issues.
- Deprecated API - Functionality that is outdated and replaced by newer, supported alternatives.
- Microservices Architecture - A modular approach where applications are split into independently deployable services.
- Jakarta EE - A modern enterprise Java framework succeeding Java EE.
- LLMs (Large Language Models) - AI models that understand and generate code or text based on training data.
- CI/CD Pipelines - Automated workflows for continuous integration, testing, and deployment.
- EJB Migration - Transforming Enterprise Java Beans into modern frameworks like Spring Boot.

Ankit Jain is a Practice Director in the Engineering HBU at Coforge, bringing over 17 years of extensive experience in the IT industry. His core expertise lies in Java technologies, with a strong foundation in cloud platforms and modern architectural patterns. Throughout his career, Ankit has worked across various domains, including telecom, finance, OTT, healthcare, and e-commerce, enabling him to deliver scalable and domain-specific solutions tailored to enterprise needs.
Related reads
About Coforge
We are a global digital services and solutions provider, who leverage emerging technologies and deep domain expertise to deliver real-world business impact for our clients. A focus on very select industries, a detailed understanding of the underlying processes of those industries, and partnerships with leading platforms provide us with a distinct perspective. We lead with our product engineering approach and leverage Cloud, Data, Integration, and Automation technologies to transform client businesses into intelligent, high-growth enterprises. Our proprietary platforms power critical business processes across our core verticals. We are located in 23 countries with 30 delivery centers across nine countries.


