Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming industries globally, with the financial sector at the forefront of this technological wave. Banks are increasingly embracing AI's potential to enhance operations, improve risk management, and gain a competitive edge. However, the adoption of AI in banking is not without its challenges, particularly in terms of regulatory compliance. One such critical framework is SR11-7, a supervisory guidance issued by the Federal Reserve (Fed) and the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC) in 2011. This article provides a comprehensive exploration of SR11-7, its impact on AI adoption in banks, and the steps banks can take to ensure compliance.
Understanding the regulatory landscape: SR11-7 explained
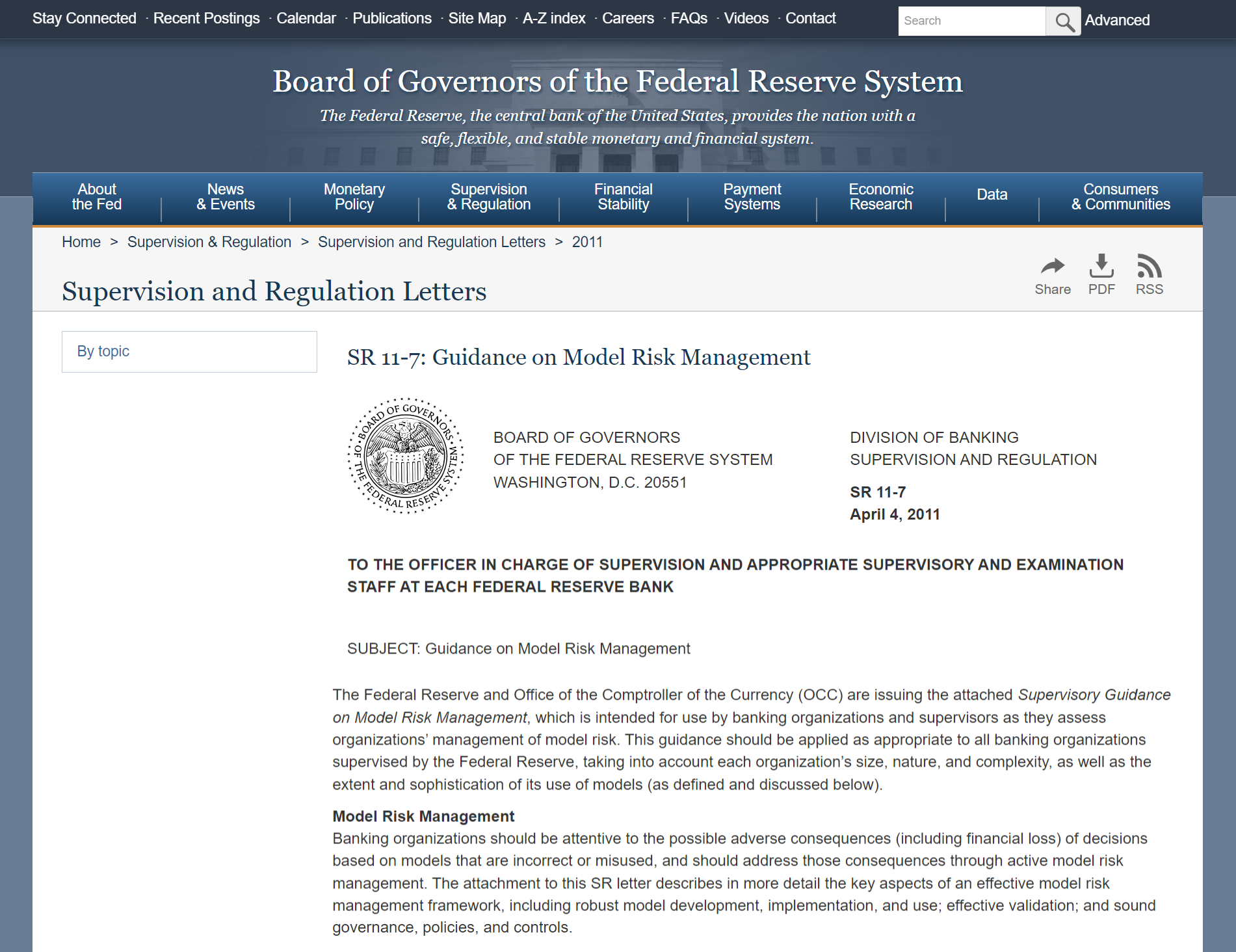
SR11-7 establishes a comprehensive framework for managing model risk, which refers to the potential for financial loss or adverse consequences arising from the use of models in banking decisions. This guidance applies to all banking organizations supervised by the Fed and the OCC, regardless of their size or complexity. It covers a wide range of models, including those used for credit risk assessment, market risk management, and regulatory compliance.
AI adoption and its impact: Navigating new possibilities and regulatory frameworks
The introduction of SR11-7 has significantly impacted the adoption of AI in the banking sector. The guidance has raised awareness of model risk and the need for robust risk management practices, prompting banks to invest in governance, policies, and controls for AI models. While this may initially increase the complexity of AI implementation, it ultimately contributes to the development of more reliable and trustworthy AI solutions.
Consequences of non-compliance: Mitigating risks and avoiding pitfalls
Failure to comply with SR11-7 can have severe consequences for banks. Regulatory penalties can be substantial, and reputational damage can be even more costly. Moreover, non-compliance can increase the likelihood of financial losses and operational failures.
A case of non-compliance: Deutsche Bank's penalty
In July 2023, Deutsche Bank faced a fine after a Federal Reserve investigation found that it failed to put in place sufficient measures to prevent money laundering. As part of the settlement, the German lender agreed to step up risk management and governance.
This incident highlights the importance of adhering to regulatory frameworks like SR11-7, by fostering a culture of strong model risk management within financial institutions.
Ensuring compliance: A step-by-step guide for banks
To ensure compliance with SR11-7, banks should take a comprehensive approach to model risk management:
- Identifying and Assessing Model Risk: Banks must identify the models they employ and assess the potential risks associated with each model. This includes evaluating model inputs, outputs, and assumptions, as well as considering potential biases and limitations.
- Developing and Implementing a Robust Risk Management Framework: This framework should include policies and procedures for model development, validation, and ongoing monitoring. Proper documentation and governance structures are crucial, with clear roles and responsibilities assigned for model oversight.
- Obtaining Independent Validation: Engaging independent experts to validate model accuracy and soundness is essential for ensuring model integrity.
- Maintaining Ongoing Monitoring: Banks must continuously monitor model performance and investigate any anomalies or unexpected results. Regular reviews and stress testing should be conducted to assess model effectiveness under different scenarios.
Embracing AI responsibly: A collaborative approach to innovation and compliance
SR11-7 plays a vital role in ensuring that banks adopt AI responsibly and manage the associated risks. By following this guidance, banks can harness the benefits of AI while mitigating risks, fostering a more secure and stable financial system. The future of banking lies in embracing AI responsibly, striking a balance between fostering innovation and adhering to regulatory frameworks. This ensures that AI empowers financial institutions to thrive in a digital world, contributing to a more robust and inclusive financial system for all participants.
Ensuring SR11-7 compliance with Quasar Responsible AI: A comprehensive Responsible AI platform
In the dynamic landscape of financial services, regulatory compliance is paramount. As AI adoption gains traction, adhering to stringent frameworks like SR11-7 is crucial for banks to navigate the complexities of model risk management.
Quasar Responsible AI, a comprehensive Responsible AI platform, emerges as a powerful ally in this endeavor.
Quasar Responsible AI seamlessly integrates with existing IT infrastructure, enabling banks to establish a robust governance framework for AI models. Its centralized model inventory provides a comprehensive overview of all AI models in use, ensuring clear lines of responsibility and effective change management.
The platform's rigorous model development process empowers banks to thoroughly document their models' purpose, assumptions, and limitations. Independent validation capabilities further reinforce the soundness and accuracy of these models, fostering trust and mitigating potential risks.
Quasar Responsible AI streamlines model implementation, ensuring seamless integration into production environments. Rigorous testing protocols safeguard against errors and ensure that models are properly documented and communicated to users.
Continuous monitoring of AI models is essential for identifying and addressing potential issues. Quasar’s comprehensive monitoring capabilities enable banks to track model performance against objectives, identify and rectify biases, and regularly review model assumptions.
Quasar’s commitment to Responsible AI extends beyond compliance, encompassing ethical considerations and fairness. The platform's explainability features provide insights into model decision-making, enabling banks to detect and mitigate potential biases.
By leveraging Quasar Responsible AI’s comprehensive capabilities, financial institutions can not only achieve SR11-7 compliance but also foster a culture of Responsible AI, ensuring that their AI initiatives are aligned with ethical principles and contribute to a fair and equitable financial ecosystem.
About Coforge
Coforge is a global digital services and solutions provider, that enables its clients to transform at the intersect of domain expertise and emerging technologies to achieve real-world business impact.
We can help refine your problem statement, crystallize the benefits, and provide concrete solutions to your problems in a collaborative model.
We would love to hear your thoughts and use cases. Please reach out to Digital Engineering Team to begin a discussion.

Deepak Saini is VP-AI. He has 24 years of IT experience with strong technology leadership experience in Generative AI, Agentic AI, Machine Learning, Deep Learning, NLP, Speech, Conversational AI, Contact Center AI, and Responsible AI.
Related reads
About Coforge
We are a global digital services and solutions provider, who leverage emerging technologies and deep domain expertise to deliver real-world business impact for our clients. A focus on very select industries, a detailed understanding of the underlying processes of those industries, and partnerships with leading platforms provide us with a distinct perspective. We lead with our product engineering approach and leverage Cloud, Data, Integration, and Automation technologies to transform client businesses into intelligent, high-growth enterprises. Our proprietary platforms power critical business processes across our core verticals. We are located in 23 countries with 30 delivery centers across nine countries.
-2.jpeg?width=1813&height=490&upsize=true&upscale=true&name=Artefact%201%20(2)-2.jpeg)

